Tanned Skin
Causes, Prevention And TreatmentTanned skin is a common condition caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. While a tan can give the skin a darker appearance, it is essentially a sign of skin damage and can lead to various skin issues over time.
Highlights
- Skin tanning is a natural process where the skin darkens in colour because of the exposure to ultraviolet light.
- Due to the resulting increase in melanin production, oxidation of melanin or rise in the number of melanocytes, the complexion may continue to darken.
- Suntanned skin is most prominent on the forehead, temples, and outer aspects of the arms.
- Sunscreen is the best defence against the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
- Any individual is prone to skin tanning, but factors such as ethnicity, age, outdoor activity, the pattern of clothing and skin type determine the extent of it.
- Anyone under the age of 5 and over 50 years can develop skin tanning due to UV ray exposure.
What Is Tanned Skin?
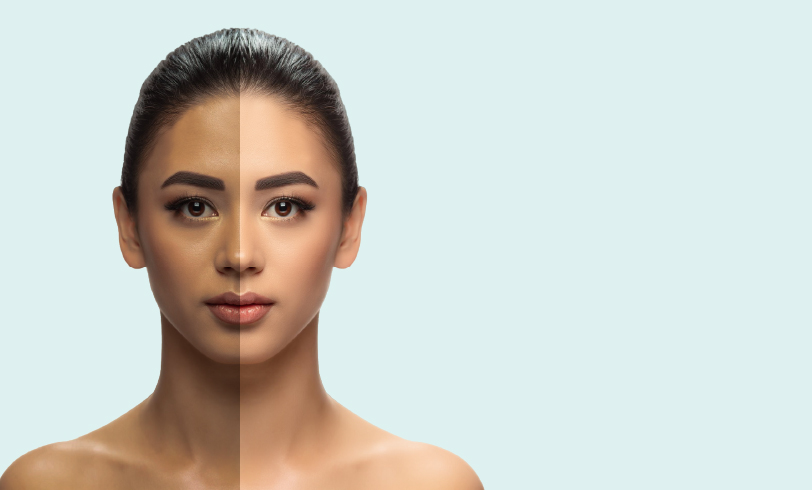
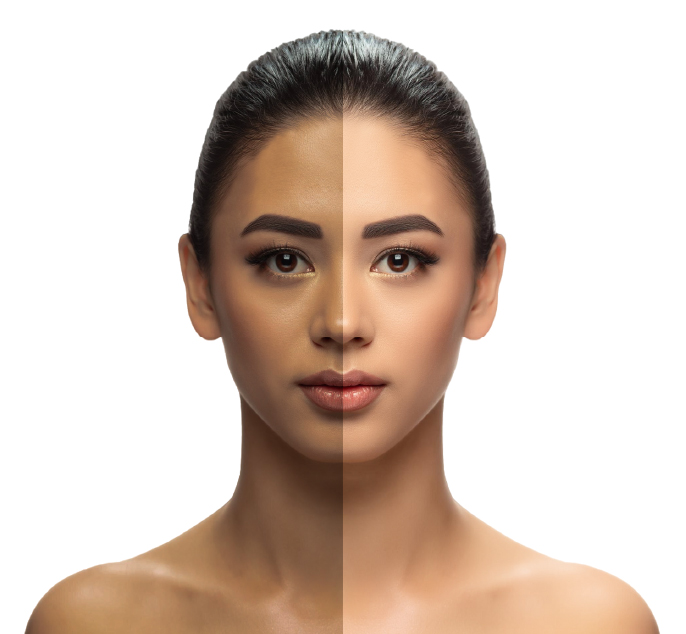
Tanned skin is skin that has darkened due to excess sun exposure, especially UV rays. It is a result of an increase in the melanin content of the skin, which is the body’s natural protective measure triggered to minimise additional skin damage. Eumelanin is the specific type of melanin that tans the skin with a brown colour.
Tanning is mostly visible on uncovered parts of the body such as the face, arms, hands, legs, feet, back and neck.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation
Here are some common reasons for stretch marks on body
-
Prolonged exposure to UV rays
-
Not using sunscreen
-
Exposure to pollutants
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Skin type
Types & Classification
-
If you have Skin Type I, you have pale white skin that may never tan.
-
If you have Skin Type II, you have a white to light beige complexion that may tan minimally.
-
If you have Skin Type III, you have a beige skin tone that may gradually tan to a light-brown colour.
-
If you have Skin Type IV, you have light brown skin, which may tan to a dark brown colour.
-
If you have Skin Type V, you have a moderately brown complexion, which may tan to a more profuse brown colour.
-
If you have Skin Type VI, you have a dark brown or black complexion that may tan generously.
Diagnosis
A dermatologist can assess and diagnose the severity of skin tan.
Examination by a dermatologist
Assessment of medical history and sun exposure habits
DermaScan to analyse the extent of skin damage
Prognosis
- Treatment can effectively reduce tanning and improve skin tone.
- Continuous sun protection and skincare routine are essential to prevent further tanning.
- Regular follow-up treatments may be necessary for maintaining results.
Are you at Risk?
-
Children below the age of 5 years and mature adults over 50 years have a reduced thickness of skin that is usually more sensitive to harmful ultraviolet radiation.
-
Individuals with immune deficiencies and chronic conditions are more vulnerable to the side effects of UV exposure.
Prevention and Management
Use a sunscreen
Avoid sun exposure
Cover your head
Wear protective clothing
Treatment Options