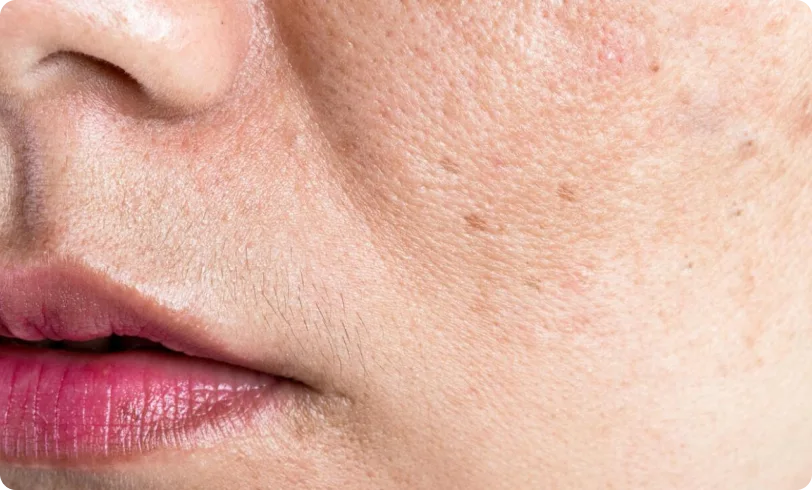
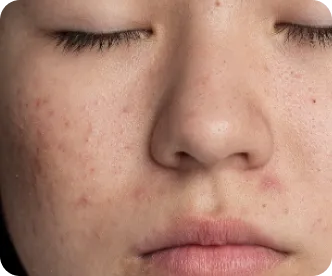
Skin Pigmentation: Causes, Symptoms And Solutions
Hyperpigmentation, more commonly known as pigmentation, occurs when certain areas of the skin become darker due to excess melanin production. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its colour. This common skin condition is often genetic and can further aggravate due to prolonged, excessive sun exposure and hormonal fluctuations. Certain medications, illnesses, and injuries can also result in uneven skin tone, dark spots and patchy complexion.
At Oliva Clinic, our dermatologists offer customised, proven and safe solutions to help you achieve an even-toned, glowing complexion.